2. Impact of Vibrio on Aquatic Animals
Prevalent Aquatic Animal Vibrio Diseases
Vibriosis stands as one of the prevalent bacterial diseases impacting shrimp, fish, and shellfish across aquatic environments. Vibrio, functioning as an opportunistic pathogen, infiltrates aquatic animals via various entry points such as the mouth, gills, and skin. This can result in primary or secondary infections, particularly during environmental deteriorations like rainy weather or significant diurnal temperature variations. Additionally, decreased resistance in aquatic animals or co-infections with other bacterial or viral diseases can exacerbate the susceptibility to Vibrio infections.
| Pathogen | ——–> Disease |
| Vibrio harveyi | – Scale loss & muscle necrosis vasculitis |
| Vibrio harveyi | – Eye lesions |
| Vibrio harveyi | – Infectious necrotizing enteritis |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | – Tail rot disease |
| Vibrio anguillarum | – Red worm disease of eel |
| Vibrio anguillarum | – Red spot disease |
| Vibrio anguillarum | – Ulcer syndrome |
| Vibrio vulnificus | – Warm-water vibriosis |
| Pathogen | ——–> Disease |
| Vibrio harveyi, Vibrio parahaemolyticus,etc. | – Abalone muscle atrophy syndrome |
| Vibrio alginolyticus, etc | Acute detachment of juvenile abalone |
| Vibrio harveyi | – Pustulosis of Haliotis discus hannai Ino |
| Vibrio harveyi | – Swollen-mouth disease of Babylonia areolata |
| Pathogen | ——–> Disease |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | – Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis syndrome of shrimp |
| Vibrio harveyi | – Luminous vibriosis of shrimp |
| Vibrio harveyi, etc | – Gill rot disease of shrimp |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio alginolyticus, etc. | – Red leg disease of shrimp |
| Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, etc. | – Vibriosis of shrimp larvae |
| Pathogens | ——–> Disease |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio alginolyticus, etc. | – Crab Vibriosis |
3. Difficulties in Vibriosis Prevention and Control:
4. Tiny but Mighty Bacteriophages

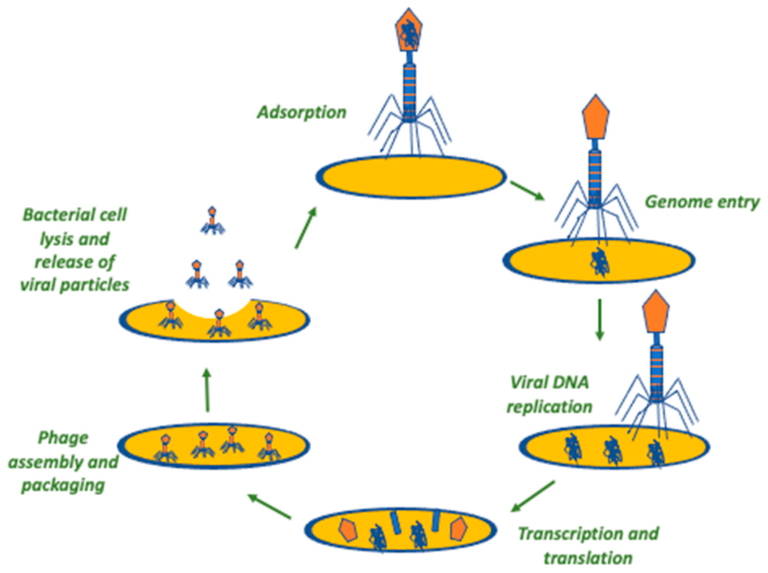
Bacteriophages, viruses that infect and reproduce within bacteria, possess the ability to specifically identify and break open bacterial cells through lysis. Their efficacy against multidrug-resistant bacteria, coupled with a reduced likelihood of inducing resistance, positions bacteriophages as a promising alternative to antibiotics. The enduring co evolutionary bond between bacteriophages and bacteria has equipped them with distinctive advantages in bacterial control.
Bacteriophage Action Mechanism
5. Unrivaled Advantages of Applying iPhage-V
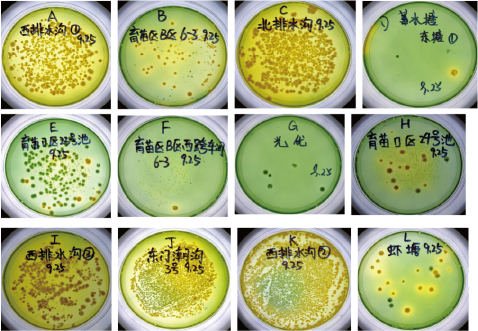
6. Selected Laboratory Isolates of Vibrio
7. Nemesis of Drug-Resistant Bacteria: iPhage-V
Targeted Pathogenic Bacteria
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Vibrio harveyi
- Vibrio alginolyticus
- Vibrio anguillarum
- Vibrio vulnificus
- Vibrio cholerae
- Vibrio campbellii
Product Information of iPhage-V
Recommended Dosage of iPhage-V
8. Efficacy Cases of iPhage-V in Treating Vibriosis
iPhage-V Treating Vibriosis Case 1
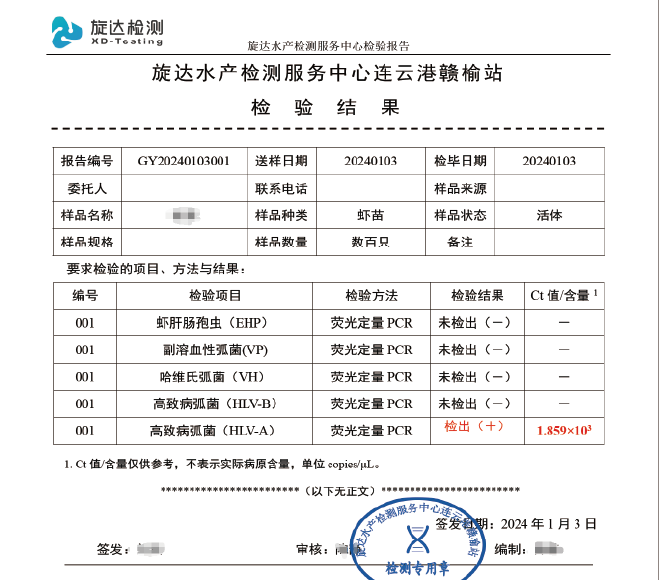
iPhage-V Treating Vibriosis Case 2
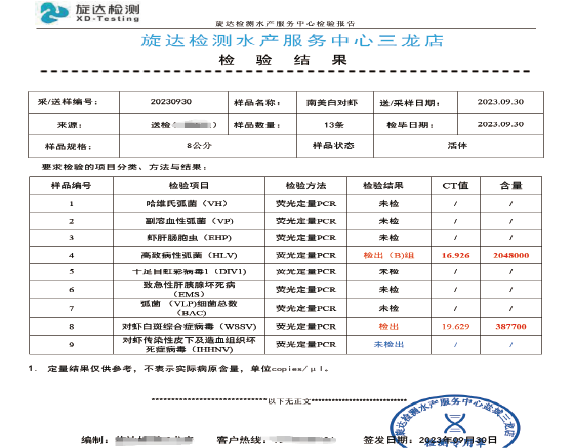
iPhage-V Treating Vibriosis Case 3
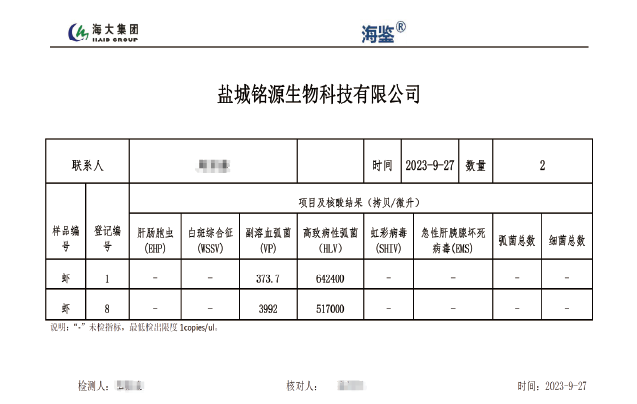
iPhage-V Treating Vibriosis Case 4
An iPhage-V Applicaiton Case of Treating Vibriosis in a Hatchery
iPhage-V Treating Vibriosis Case 5
An iPhage-V Applicaiton Case of Treating Vibriosis in a Shrimp Nursery
8. Advantage Comparison of iPhage-V & Other “Phage-based” Products
| Aspects | iPhage-V | Other “Phage-based” Products |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Tolerance | iPhage-V can endure up to 90°C. | Others, in liquid form, are usually not resistant to high temperatures, may require refrigeration. |
| Bacterial Coverage | iPhage-V covers over 85% of pathogenic bacterial strains. | Others have been found out only to cover between 20% and 30% of pathogenic bacterial strains. |
| Shelf Life | Our specially formulated, powdered iPhage boasts an extended shelf life of at least 12 months. | Others, in liquid,may have a shorter shelf life due to their susceptibility to bacterial contamination, typically lasting only 40 to 80 days after opening. |
| Targeted Treatment | iPhage treatment effectively addresses a range of high-impact diseases, including high pathogenic Vibrio, EMS, and Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Syndrome. Long-term use can also help prevent these diseases and reduce high mortality rates. | Our commitment to maintaining the industry’s most comprehensive bacterial library and phage banks fuels continuous innovation, ensuring we stay ahead of evolving threats. |
