In 2023, a total of 16,890 market samples were received by the R&D center. The collected samples were categorized based on different animal sources, with chicken source samples having the highest collection rate. When analyzed by region, samples from the Northeast region had the highest quantity. In total, 6,189 strains were isolated from the collected samples, among which E. coli and Salmonella had the highest isolation rates, followed by Clostridium, Staphylococcus aureus, and Riemerella anatipestifer. All isolated strains were characterized and analyzed based on serotype, virulence genes, and other factors, and were ultimately incorporated into the Shandong New Line Popular Pathogen Isolate Bank.
Figure 1. Sample regional distribution in 2023 (16,890 samples)
Figure 2. Sample animal source distribution in 2023 (16,890 samples)

Figure 3. Pathogen isolation in 2023 (6,189 pathogens isolated)

The rational use of antibiotics is of great significance in preventing the development of bacterial resistance. Inappropriate or excessive use of antibiotics can lead to rapid development of resistance in bacteria, thereby reducing the effectiveness of antibiotics, increasing the difficulty of treatment, and causing some originally curable diseases to become difficult to cure. In addition, antibiotic abuse can also cause adverse consequences such as intestinal flora imbalance and allergic reactions.
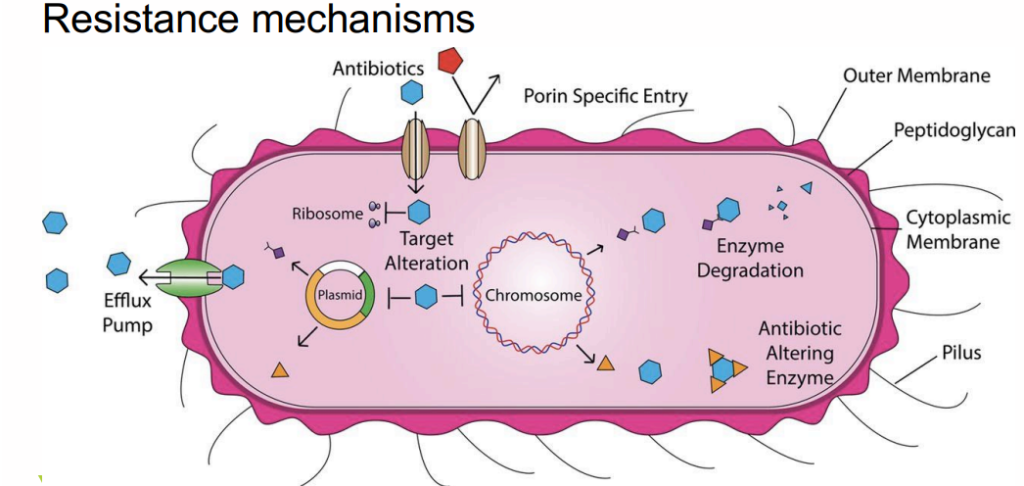
Antibiotic resistance mechanism

The most commonly isolated E. coli and Salmonella strains from the market samples collected in 2023 were statistically analyzed for their resistance rates. Data showed that when antibiotics were used according to the recommended dosage, the resistance rate was relatively high, with an average of over 50%, and a trend of multidrug resistance was observed.
Figure 4. Resistance rate of E. coli to 8 common antibiotics in the market

Figure 5. Statistics on Drug Resistance of Salmonella to 8 Commonly Seen Antibiotics in the Market

It should be noted that Salmonella belongs to facultative intracellular parasites, which can survive in the environment and animal intestines, and can also parasitize in intestinal epithelial cells and macrophages, forming “escaped bodies” to avoid antibiotics. Persecution, the concentration of antibiotics in the blood or cells is difficult to reach MBC, so it is difficult to achieve ideal results in the purification or treatment of Salmonella by antibiotics alone.
The problem of bacterial drug resistance has become one of the major causes of huge economic losses in the animal husbandry industry. With the comprehensive ban on antibiotics in feed in 2020, products and technologies for reducing antibiotics and replacing antibiotics have emerged in an endless stream. In addition to the traditional Chinese veterinary medicine, micro-ecological preparations, enzyme preparations, etc. that we are familiar with, antibacterial peptides, fermented feed, etc., bacteriophages have also become a new alternative to antibiotics and have become the focus of attention. Bacteriophages are specific viruses of bacteria and the natural enemies of bacteria. They are widely found in nature. They are specific to bacteria and each bacteriophage has its own host bacteria. In addition, the bactericidal mechanism of bacteriophages is completely different from that of antibiotics and vaccines. It is an ideal means to kill drug-resistant pathogens and antigen-variant pathogens.
The bacteriophage-antibiotic synergistic effect (PAS) is a new therapeutic strategy to solve the problem of bacterial drug resistance, among which sublethal concentrations of antibiotics can greatly increase the ability of lytic bacteriophages to produce themselves. This synergistic effect can produce an “ordered” effect, so that bacteriophage treatment before antibiotics can achieve the maximum killing effect, optimizing the administration time of combination therapy to enhance its efficacy.
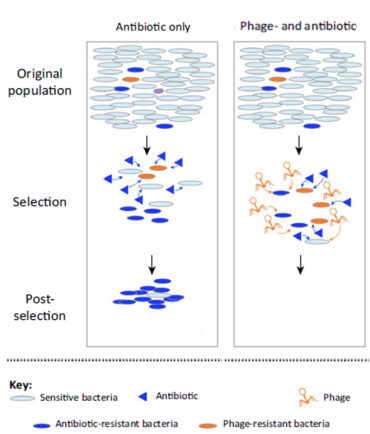
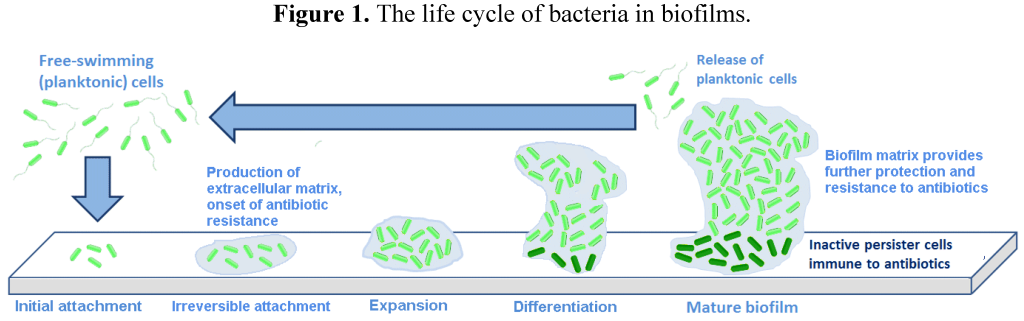
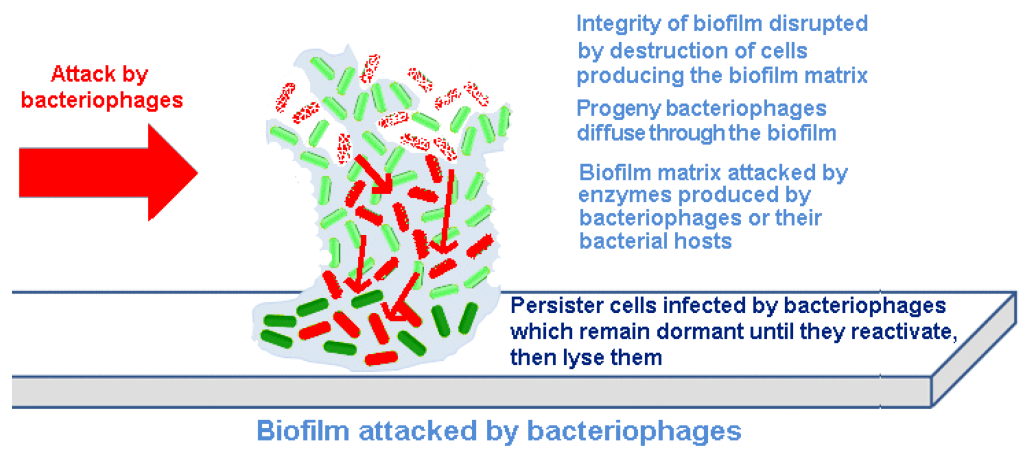
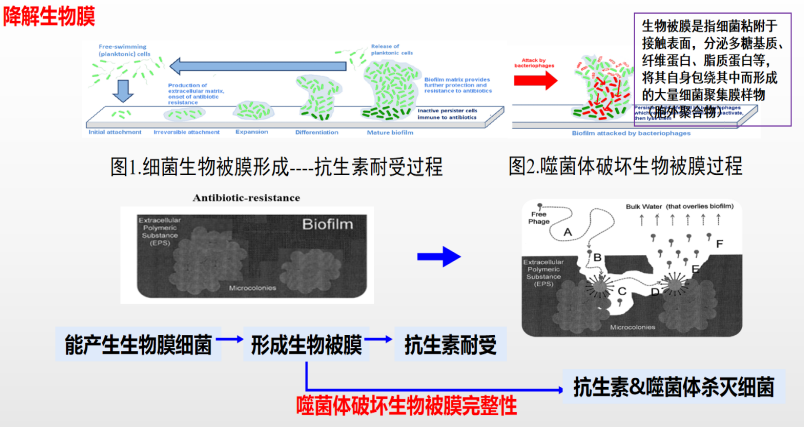
Figure 6. Bacteriophage & Antibiotics Synergistic Effect

Shandong New Line Biotechnology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research and development and sales of bacteriophage products. It has jointly established the Bacteriophage Industry Research Institute with the Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, relying on the International Bacteriophage Research Center, and formed a research and development team with more than 30 doctors and masters as the main backbone, and cooperates with Chinese Academy of Sciences, South Korean CTC Company, etc., to solve the problem of drug-resistant bacteria in multiple fields such as animal husbandry and agriculture by using bacteriophage biological solutions.
